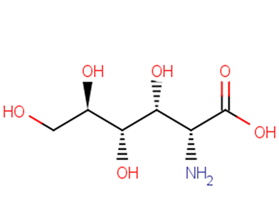
D-Glucosaminic acid
CAS No. 3646-68-2
D-Glucosaminic acid( 2-Amino-2-deoxy-D-gluconic acid )
Catalog No. M19722 CAS No. 3646-68-2
D-Glucosaminic Acid is a useful starting material for the synthesis of aldonic acids.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 133 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 203 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 353 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameD-Glucosaminic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionD-Glucosaminic Acid is a useful starting material for the synthesis of aldonic acids.
-
DescriptionD-Glucosaminic Acid is a useful starting material for the synthesis of aldonic acids.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms2-Amino-2-deoxy-D-gluconic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3646-68-2
-
Formula Weight195.17
-
Molecular FormulaC6H13NO6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESN[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
SHIN1
SHIN1 is an inhibitor of human serine hydroxymethyltransferse 1(SHMT1) with IC50 of 5 nM and human serine hydroxymethyltransferse 2 (SHMT2) with an IC50 of 13 nM.
-
Hosenkoside C
Hosenkoside C is a baccharane glycoside isolated from the seeds of Impatiens balsamina.
-
3,4-Dimethoxybenzami...
3,4-Dimethoxybenzamide, amide, is isolated from the solid culture of Streptoverticillium morookaense. 3,4-Dimethoxybenzamide can be used as the starting material to preparation Itopride hydrochloride.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


